Study in Germany CONSULTANTS
-Experience Excellence-
Table of Contents: Study in Germany Consultants
- Studying Bachelor's Degree Programs in Germany
- Studying in Germany: Start with a Public University's Studienkolleg!
- Fast-Track Studienkolleg: an all-in-one-year foundation
- Studying for a bachelor’s degree in Germany through the lowest-cost pathway!
- Study in Germany: English taught degree & studienkollge
- Studying Medicine in Germany at Public Universities
- Studying Medicine in Germany in English at Private Universities!
- Other Medical Programs after M Course Foundation!
- Study B.Sc. Nursing at a German Public University.
- B.Sc. Dual Studies in Nursing
- Pursuing Nursing through Ausbuildung in Germany
- AUSBILDUNG in Germany!
- Eligibility for Ausbildung in Germany!
- English-taught Master's
- MBA Specialisations
- German-taught Master's : More acceseble, benificial and a systematic preparation
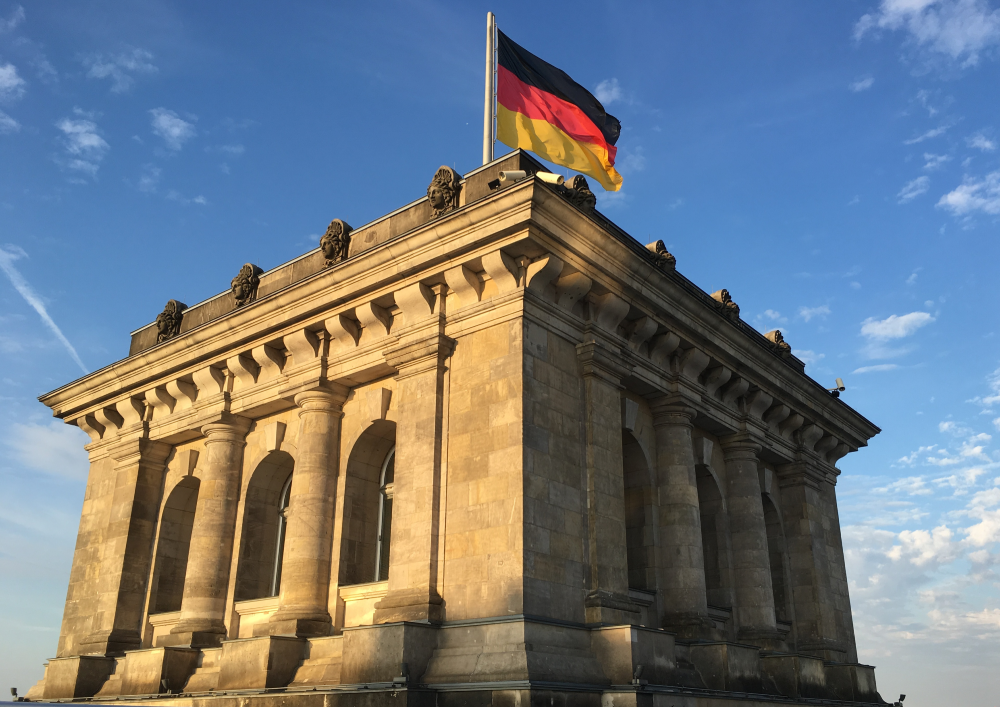

Table of Contents
Study Germany Consultants and their importance
Your Gateway to World Class Education
Germany is most popular among international students now. Thus the need of expert German education consultants. Thus the German education consultants! German universities offer world-class education at affordable costs.
One primary reason students choose Germany is its free or low-cost tuition. Public universities charge little to no fees, even for international students.
Quality education, career opportunities, and a clear path to permanent settlement make studying in Germany a top choice for students worldwide.
Many universities have close ties with industries, giving students access to internships and hands-on experience. Graduates from German universities are highly valued in the global job market. Germany also has a strong economy and offers excellent job opportunities after graduation.
After completing their studies, students can stay in Germany for 18 months to find a job. This pathway often leads to permanent residency and, eventually, citizenship, providing a clear and promising career path.
Life in Germany is not just safe but also vibrant and diverse. The country’s high standard of living, efficient public transport, and rich cultural history make it an exciting place to live. International students can enjoy vibrant cities, historical landmarks, and beautiful countryside, all within a safe and secure environment. Study in Germany consultants are your first contact point to gather all the information you need to start with.
The Best Studying in Germany Consultants
#ThinkGermanyThinkKcr

Study in Germany
Bachelor's Degree Programs
Germany is home to nearly 450 universities offering 20,000+ study programs, with a significant focus on bachelor's degrees. Known for its high-quality education and affordability, many public universities provide tuition-free or low-cost programs, making studying in Germany an excellent and unique choice for international students.
Studying in German or English, international students can access diverse fields of study, global recognition, and career opportunities.
Discover how Germany's practical and innovative learning environment can shape your future by pursuing a bachelor's degree at a German university.

Studying Bachelor's Degree Programs in Germany
Germany is home to nearly 450 universities offering 20,000+ study programs, with a significant focus on bachelor's degrees. Known for its high-quality education and affordability, many public universities provide tuition-free or low-cost programs, making studying in Germany an excellent and unique choice for international students.
Studying in German or English, international students can access diverse fields of study, global recognition, and career opportunities.
Discover with the expert study in Germany consultant how Germany's practical and innovative learning environment can shape your future by pursuing a bachelor's degree at a German university.
Studying in Germany: Start with a Public University's Studienkolleg!
If you plan to study in Germany, KCR, the best study in Germany consultant, recommends attending a public university’s Studienkolleg. This foundation year is perfect for international students whose high school qualifications don’t match German university standards.
It prepares you for direct admission to a bachelor’s program at the same public university. With streamlined admissions, affordable tuition, and a seamless academic progression, the public university’s Studienkolleg is your gateway to quality education in Germany.

Start studying in Germany
at a Public University's Studienkolleg!
If you plan to study in Germany, KCR, the best study abroad and overseas education consultants, recommends attending a public university’s Studienkolleg. This foundation year is perfect for international students whose high school qualifications don’t match German university standards.
It prepares you for direct admission to a bachelor’s program at the same public university. With streamlined admissions, affordable tuition, and a seamless academic progression, a public university’s Studienkolleg is your gateway to quality education in Germany.

Fast-Track Studienkolleg: an all-in-one-year foundation
Starting your studies in Germany with the Fast-Track Studienkolleg reduces the time required to complete your language and Foundation to just a year. This way, you can begin your university degree studies in your second year in Germany!
- No German language levels are required to apply for this program!
- Start learning German from the zero Level from the Studienkolleg online while you are in your country of current residence.
- After completing the A2 Level online from the Studienkolleg, you can apply for a visa and arrive to study in Germany; you can attend an all-in-one-year Foundation program that includes B1, B2, and C1 level Germany classes and relevant subjects as applicable.
- In this All-In-One package, the Studienkolleg takes care of students for the entire year, meeting them upon arrival at the nearest international airport and transferring them to pre-arranged furnished hostel accommodations.
- The fast-track Studienkolleg package also includes a monthly stipend of 370.EUR for food and other living expenses for the entire 12 months, study materials, exam fees, resident permit fees, and second-year visa extension fees as students progress to the University. Contact KCR, the best among the study in Germany consultants to know in detail and apply.

Studying in Germany
through an
all-in-one-year
Fast-Track Studienkolleg!
Starting your studies in Germany with this Fast-Track Studienkolleg reduces the time required to complete your language and Foundation to just a year. This way, you can begin your university degree studies in your second year in Germany!
- No German language levels are required to apply for this program!
- Start learning German from the zero Level from the Studienkolleg online while you are in your country of current residence.
- After completing the A2 Level online from the Studienkolleg, you can apply for a visa and arrive to study in Germany; you can attend an all-in-one-year Foundation program that includes B1, B2, and C1 level Germany classes and relevant subjects as applicable.
- In this All-In-One package, the Studienkolleg takes care of students for the entire year, meeting them upon arrival at the nearest international airport and transferring them to pre-arranged furnished hostel accommodations.
- The fast-track Studienkolleg package also includes a monthly stipend of 370.EUR for food and other living expenses for the entire 12 months, study materials, exam fees, resident permit fees, and second-year visa extension fees as students progress to University.

Studying for a bachelor’s
degree in Germany through
the lowest-cost pathway!
- By choosing this pathway, you can study for a degree in Germany at a public university and attend a State-Funded Studienkolleg for free!
- Upon arrival, you will start learning German in a German environment, even from zero or based on your current language level.
- You may even pay the language course fees monthly unless the German consulate asks you to pay in advance and provide a receipt while processing your visa application.
- The cost of the language course is the lowest in Germany.
- You will learn the German language from certified language teachers in Germany at an approved language center.
- You can register with the State-funded Studienkolleg upon achieving the required language level through this low-cost pathway to study in Germany.

Studying for a bachelor’s
degree in Germany through
the most low-cost pathway!
- By choosing this pathway, you can study for a degree in Germany at a public university and attend a State-Funded Studienkolleg for free!
- Upon arrival, you will start learning German in a German environment, even from zero or based on your current language level.
- You may even pay the language course fees monthly unless the German consulate asks you to pay in advance and provide a receipt while processing your visa application.
- The cost of the language course is the lowest in Germany.
- You will learn the German language from certified language teachers in Germany at an approved language center.
- You can register with the State-funded Studienkolleg upon achieving the required language level through this
low-cost pathway to study in Germany.

Study in Germany:
English taught degree & studienkollge
- Those with 50%+ marks in higher secondary school education can apply.
- IELTS and APS are not required while applying for admission.
- No tuition fees are charged for the English-taught degree program offered at a public university.
The shorter (8-month) Foundation Program is entirely taught in English and designed to lead to the winter semester/October University Intake! By choosing this package of studies in Germany that includes an English-taught Foundation and tuition-free degree, you complete a Foundation for a bachelor’s degree in the shortest period- just 8 months! The best and experienced study in Germany consultants who are the authorised representatives can facilitate your application for a place and visa.

Studying in Germany for a B.Eng.
Degree taught in English and tuition-free,
after an English-taught Foundation!
- Those with 50%+ marks in higher secondary school education can apply.
- IELTS and APS are not required while applying for admission.
- No tuition fees are charged for the English-taught degree program offered at a public university.
The shorter (8-month) Foundation Program is entirely taught in English and designed to lead to the winter semester/October University Intake! By choosing this package of studies in Germany that includes an English-taught Foundation and tuition-free degree, you complete a Foundation for a bachelor’s degree in the shortest period- just 8 months!
Study Medicine in
Germany
#ThinkGermanyThinkKcr

Studying Medicine in
Germany at Public Universities
As you heard right, studying medicine at most German Public Universities is tuition-free. The state-funded universities in Baden Wurttemberg alone charge a nominal tuition fee of 1500. EUR per semester!
Public universities teach medicine entirely in German, and those who want to study medicine for free at public universities must attend a Medical Foundation course offered at a Studienkolleg. Since the M course is offered at a Studienkolleg in the medium of German, the studies in Germany starts with German language courses from zero level or from the current Level on arrival in Germany. Experienced German education consultants can guide you from the scratch to attending an M Foundation course and qualify for a Medicine university program!

Studying Medicine at
Public Universities in Germany
As you heard right, the medicine course is also offered tuition-free at most German public universities. The state-funded universities in Baden Wurtumburg alone charge a nominal tuition fee of 1500. EUR per semester!
Meanwhile, private medical universities in Germany charge approximately 26,000 – 35000.EUR per year!
Public universities teach medicine entirely in German, and student applicants must first attend a foundation offered at a Studienkolleg. Most Studienkolleg ask for a particular level of German knowledge to be accepted for a Foundation course. However, a few even provide German language classes at zero level.

Studying Medicine in Germany
in English at Private Universities!
Studying medicine in Germany in English is also possible—at German Private medical universities, which accept students without any German language knowledge.
However, better English language skills are a must.
Since the clinical studies start after two-three years students learn the German language and earn necessary skills. Students can attend optional language courses offered at the university, and also improve skills while in Germany.
However, all the studies were conducted and assessed in English only!
Private medical universities in Germany can charge tuition as per the law, and the fees range from 26,000 to 35,000 EUR per year. The application process becomes easy when a best study in Germany consultants handle your application!

Studying Medicine at Private Universities in Germany!
Private medical universities in Germany accept students directly without any German language knowledge, and there is no need to attend a foundation course.
However, better English language skills are a must.
Since the medical course’s non-clinical studies take two years to complete, students also learn the necessary skills in German, which helps them while attending clinical studies in German teaching hospitals.
However, all medicine studies were conducted and assessed in English only!
Other Medical Programs
after M Course Foundation!
Suppose you are not interested in medicine and are particularly interested in studying at a public university in Germany. In that case, you can choose any other suitable medical program from the list below!
- Medicine technology
- Biosystems technology
- Biochemistry
- Biophysics
- Pharmacy
- Science of nutrition
- Veterinary medicine
- Psychology
- Molecular biology
- Medicine and biomedical sciences
- Applied biomedical sciences

Other Medical Education
Programs after M Course, Foundation
After M-Course Foundation, one can also consider pursuing the below-listed bachelor’s degree programs in Germany
- Dentistry
- veterinary medicine
- Psychology
- Molecular biology
- Medicine and biomedical sciences
- Applied biomedical sciences
- Medicine technology
- Biosystems technology
- Biochemistry
- Biophysics
- Pharmacy
- Science of nutrition
Three Ways to Study Nursing in Germany!
Choose the path best suits your goals and start your
Nursing Studies in Germany

Option 1:
Study B.Sc. Nursing at a
German Public University.
The traditional path to becoming a nurse in Germany is to study for a B.Sc. Nursing program at a Public University.
You will start with German language courses, aiming to achieve B1/B2/C1 level skills and proficiencies. After completing the required level, you will also follow an M Course foundation at a Studienkolleg as scheduled and stated in the conditional letter received from the University.

1. Bachelor’s in Nursing
(B.Sc.) at Public Universities
The traditional path to becoming a nurse in Germany is through a B.Sc. in Nursing from a public university.
You’ll first need to complete an M Course or Foundation Program at a Studienkolleg to qualify.
If you need German language skills at the B1/B2 level, you’ll start with language classes before progressing to the M Course.

Option 2:
B.Sc. Dual Studies in Nursing
A few public universities offer B.Sc. dual studies in Nursing in partnership with established healthcare service-providing employers in Germany. To pursue nursing in Germany through the B.Sc. dual studium, as mentioned in option 1, you must complete an M Course Foundation to qualify for acceptance by one of the University’s panel employers. Once accepted by the employer, you will automatically meet the university’s remaining conditions for a direct acceptance to the B.Sc. dual studium program.

3. Dual Study
Bachelor’s in Nursing
Some public universities also offer a dual study B.Sc. in Nursing in partnership with healthcare employers. Like the regular B.Sc., you must complete an M Course Foundation first.
Afterward, you’ll apply to the university and its healthcare partner for this integrated program.

Option 3:
Pursuing Nursing through Ausbuildung in Germany
Today’s most popular choice for nursing studies in Germany is Ausbildung, a hands-on apprenticeship training offered by hospitals and other healthcare settings in collaboration with German training schools.
This direct vocational training program doesn’t require a Foundation/Studienkolleg course.
In addition, during the direct three years of training, you’ll also receive a monthly stipend.
To be eligible, you must achieve a B1/B2 level in German before being accepted.
Experienced study in Germany consultants in nursing programs can provide you the best services.

2. Ausbildung: Nursing
Apprenticeship Training!
Today’s most popular choice is Ausbildung, a hands-on apprenticeship offered by hospitals and healthcare institutions in collaboration with German training schools.
This direct program doesn’t require an M Course or Foundation Program. During the three years of training, you’ll also receive a monthly stipend.
To be eligible, you must achieve a B1 level in German in your home country before applying.
Choose what you like learning best and let someone pay you to learn it!
#ThinkGermanyThinkKcr

AUSBILDUNG
in Germany!
Instead of studying in Germany for a degree first and hunting for internships or apprenticeships to qualify for jobs, you can directly jump into a job training program in Germany.
This program gets you ready to start working right away!
This particular job training is known as “Ausbildung in German.” It lasts three years and emphasizes on-the-job learning. Once you finish, you’ll have a vocational qualification recognized by employers all over Germany and Europe.
And guess what? There are no tuition fees for the Ausbildung program! Plus, you’ll even get paid a monthly allowance while you’re learning.

AUSBILDUNG
in Germany!
Instead of getting a degree and hunting for internships or apprenticeships to qualify for jobs, you can directly jump into a job training program in Germany.
This program gets you ready to start working right away!
This particular job training is known as “Ausbildung.” It lasts three years and is mainly done on the job. Once you finish, you’ll have a vocational qualification recognized by employers all over Germany and Europe.
And guess what? There are no tuition fees for the Ausbildung program! Plus, you’ll even get paid a monthly allowance while you’re learning.

Eligibility for
Ausbildung in Germany!
To qualify for an Ausbildung program in Germany;
1. You must have completed higher secondary (12th grade) education,
2. Start learning German and continue until you pass a B1/B2 Level German test (if you haven’t attained it yet).
3. Most participating employers generally look for new trainees under 29 years old, but no age limit is officially set for Ausbildung in any occupation.
4. It’s crucial to have a genuine interest in training in your chosen occupation. This interest and your eagerness to become a skilled worker or professional in the same occupation will inspire and motivate you throughout the Ausbildung program.
5. If you’ve interned, worked, or have any additional education in the same field, such as a diploma or degree will add more value to your application.
Ausbildung is offered in 350+ occupations in almost all businesses, industries, and sectors. KCR the first study in Germany consultants which introduced Ausbildung admission services are the source for guidance on this apprenticeship program!

Eligibility for
Ausbildung in Germany!
To qualify for an Ausbildung program in Germany;
1. You must have completed higher secondary (12th grade) education,
2. Start learning German and continue until you pass a B1/B2 Level German test (if you haven’t attained it yet).
3. Generally, most participating employers look for new trainees below 29 years old, but no age limit is set officially for Ausbildung in any occupation.
4. It’s crucial to have a genuine interest in training in your chosen occupation. This interest and your eagerness to become a skilled worker or professional in the same occupation will inspire and motivate you throughout the Ausbildung program.
5. If you’ve interned, worked, or have any additional education in the same field, such as a diploma or degree will add more value to your application.
Ausbildung is offered in 350+ occupations in almost all businesses, industries, and sectors.
Studying in Germany for a Master's Degree
#ThinkGermanyThinkKcr

English-taught Master's
Germany’s public universities also offer English-taught programs, fondly called international programs.
- Generally, a minimum 2.5 German GPA is required to qualify.
- Some universities accept applications with less than a 2.5 GPA
- Most universities ask for an IELTS test passed certificate with a 6.5 overall score for language skills.

Study an English-taught
Master's in Germany
Germany’s public universities offer English-taught programs, fondly called international programs.
- Generally, at least a 2.5 German GPA is required to apply.
- Some universities accept applications with less than a 2.5 GPA
- Most universities ask for an IELTS score for language skills.

Study Master's in Private
Universities : The German Education Consultants make it the process quicker and simpler!
You can access low-cost, high-quality degree programs at German private universities tailored to international students. Choose from. one-year MBA (General) or 18-month MBA specializations designed for professionals with:
- A degree with 50% or more marks,
- One year of work experience in any field and
- 6.0 IELTS or equivalent English proficiency.
MBA Specialisations through the best study in Germany consultants!
- MBA International Business
- MBA Marketing Management
- MBA Management Consulting
- MBA Project Management
- MBA Shipping and Logistics
- MBA Sales Management
- MBA Sustainable Water Management
- MBA Financial Management
- MBA Financial Risk Management
- MBA Investment Banking
- MBA Digital Technology
- MBA Sports Management
- MBA Health Service Management
- MBA Health & Safety Leadership
- MBA Digital Health Transformation
- MBA Diplomacy
Explore additional Master's degree programs (1 year, 18 months, or 2 years) across diverse fields. With a relevant bachelor's degree, 50%+ marks, and 6.0 IELTS, you can advance your career with a degree from Germany.
- MSc Psychology Coaching & Counselling
- MSc Strategic and International Business Management (Double Degree)
- MSc International Marketing (Double Degree)
- MSc Asset Management
- MSc International Logistics & Transportation Management
- MSc International Public Health Management
- MSc Software Engineering
- MSc Data Science
- MSc Digital Transformations
- MA Generative Design & AI
- MA New Media Design
- MA Visual & Experience Design
- MA Communication Design
- MA New Media Design
- MA Innovation Design Management
KCR CONSULTANTS partner with a diverse network of premier private German universities. As an expert study in Germany consultants KCR offers you comprehensive, reliable information and expert guidance throughout the application process, ensuring you secure your place in your chosen program.

Study Master's in Private
Universities in Germany
You can access low-cost, high-quality degree programs at German private universities tailored for international students. Choose from one-year MBA (General) or 18-month MBA specializations designed for professionals with:
- A degree with 50% or more marks,
- One year of work experience in any field and
- 6.0 IELTS or equivalent English proficiency.
MBA Specialisations
- MBA International Business
- MBA Marketing Management
- MBA Management Consulting
- MBA Project Management
- MBA Shipping and Logistics
- MBA Sales Management
- MBA Sustainable Water Management
- MBA Financial Management
- MBA Financial Risk Management
- MBA Investment Banking
- MBA Digital Technology
- MBA Sports Management
- MBA Health Service Management
- MBA Health & Safety Leadership
- MBA Digital Health Transformation
- MBA Diplomacy
Explore additional Master's degree programs (1 year, 18 months, or 2 years) across diverse fields. With a relevant bachelor's degree, 50%+ marks, and 6.0 IELTS, you can advance your career with a degree from Germany.
- MSc Psychology Coaching & Counselling
- MSc Strategic and International Business Management (Double Degree)
- MSc International Marketing (Double Degree)
- MSc Asset Management
- MSc International Logistics & Transportation Management
- MSc International Public Health Management
- MSc Software Engineering
- MSc Data Science
- MSc Digital Transformations
- MA Generative Design & AI
- MA New Media Design
- MA Visual & Experience Design
- MA Communication Design
- MA New Media Design
- MA Innovation Design Management

German-taught Master's : More acceseble, benificial and a systematic preparation
- A 50% minimum mark in a bachelor’s degree meets the admission criteria for many courses.
- Starting with German language studies, prepare to get ready to progress to the master’s Degree later.
German Public Universities accept various levels of German proficiency:
- C1 Level: Direct admission to a master’s program.
- B2 Level: attend C1 Level classes/DSH Tes preparatory classes at an approved language school in Germany first.
- B1 Level: Complete the remaining B2&C1 levels in Germany.
- A2 Level: Start with B1 Level classes and achieve a C1 Level at a university-suggested language center in Germany
- A1 Level: You must attend A2-C1 Level classes to qualify for the Master’s Degree course
- Zero Level: Start from A1.1 Level language learning in Germany, and improve the levels steadily until you attain a proficiency level before progressing to the Master’s degree studies!
The experienced German education consultants ensure you receive the best support and guidance to migrate and achieve your goal of studying in Germany and qualifying for a master’s degree from a German university.

German-taught Master's programs: more accessible!
- A 50% minimum mark in a bachelor’s degree meets the admission criteria.
- Language proficiency is needed in German (C1 level), but one can start with German language studies and progress to the master’s Degree later.
Along with conditional offers, German public universities accept various levels of German proficiency:
- C1 Level: Direct admission to a master’s program.
- B2 Level: attend C1 Level classes/DSH Tes preparatory classes at an approved language school in Germany first.
- B1 Level: Complete the remaining B2&C1 levels in Germany.
- A2 Level: Start with B1 Level classes and achieve a C1 Level at a university-suggested language center in Germany
- A1 Level: You must attend A2-C1 Level classes to qualify for the Master’s Degree course.
- Zero Level: Start from A1.1 Level language learning in Germany, and improve the levels steadily until you attain a proficiency level before progressing to the Master’s degree studies!
At KCR, we ensure you receive the best support and guidance to migrate and achieve your goal of pursuing a master’s degree while experiencing the world-famous German higher education system!
Pursue PG Medicine or Dentistry in
Germany
#ThinkGermanyThinkKcr
Germany is among the few countries best suited to pursue PG medicine or dentistry, which is called “Specialization.” The training is fully hospital-based, offering hands-on experience while working towards becoming a specialist. International medical and dental graduates must be licensed in Germany before qualifying for specialised training in German hospitals and clinics.
Why Choose Germany to pursue PG medicine or dentistry?
Germany currently needs more qualified healthcare professionals, including doctors and dentists. All 16 German Federal states have introduced initiatives to attract foreign-trained professionals to address this.
Almost all German states have been offering a ‘Grant,’ exclusively introduced to encourage qualified foreign-educated doctors and dentists. The grant covers most of the cost of preparatory programs, often called the “Doctors’ Program.”
The Federal Employment Agency also offers free assistance with licensing and job searches individually to make it easier and more attractive!
The Doctors' Program
Learn German
- Start with general German language classes.
- Achieve a B2 level to join medical German language courses.
- Learn workplace-specific medical terminology.
Medical Language Test
- Upon passing the test, you will be considered qualified for a temporary medical license.
- This allows you to work under the supervision of a registered doctor for up to 2 years
Deficit Letter
- Your health professional qualification from a foreign country will be assessed during this time.
- You’ll receive a “Deficit Letter” confirming eligibility for licensing and grants.
Licensing Pathways
For Registered Doctors
- Complete the assessment process and licensing before moving to Germany. A Deficit Letter qualifies you for state grants.
For Fresh Graduates
- Start the licensing process after arriving in Germany while attending the Doctors’ Program.
Preparing Your Documents
Translate Documents
- All qualifications must be translated into German by a state-approved translator (only available in Germany).
Certify Documents
- Genuine copies of documents must be certified by the German Consulate in your country or local officials in Germany.
Comprehensive Support Services
KCR CONSULTANTS provides comprehensive support services to ensure your success in Germany. Our services include:
- Personalized Counseling: KCR offers one-on-one counselling sessions to help you understand your goals and preferences and choose the best educational path.
- Application Assistance: The expert German Education Consultants guide you through the application process, from selecting the right universities to submitting your applications.
- Visa Guidance: We assist you in obtaining the necessary visas and permits, ensuring a hassle-free move to Germany.
- Accommodation Support: Finding suitable accommodation can be challenging. We help you secure comfortable and affordable housing options.
- Cultural Orientation: We provide sessions to help you adapt to the German culture and lifestyle, making your transition smoother.
#ThinkGermanyThinkKcr
Pursuing Non-Clinical PG Medicine in
Germany for Non-FMGE Medical Graduates!
Studying in Germany for a PG is still possible those who studied medicine or dentistry abroad and are not yet registered doctors. You can benefit from non-clinical English-taught Master’s programs offered by German Public or private Universities.
Ideal for those who never prepared for the FMGE, don’t want to sit the test, or who couldn’t clear it, these programs offer valuable opportunities:
The benefits:
- Work part-time during your studies.
- Stay in Germany post-graduation to seek employment.
- Begin your journey toward medical licensure in Germany.
Start your journey with us best study in Germany consultants, today!
Studying in Germany for a PG is still possible those who studied medicine or dentistry abroad and are not yet registered doctors. You can benefit from non-clinical English-taught Master’s programs offered by German Public or private Universities.
Ideal for those who never prepared for the FMGE, don’t want to sit the test, or who couldn’t clear it, these programs offer valuable opportunities:
The benefits:
- Work part-time during your studies.
- Stay in Germany post-graduation to seek employment.
- Begin your journey toward medical licensure in Germany.
Start your journey with us best study in Germany consultants, today!
MBBS or Medicine graduates, especially those who studied medicine abroad and are not yet registered doctors, can benefit from English-taught Master’s programs offered by German public universities.
Ideal for those who never prepared for the FMGE, don’t want to sit the test, or who couldn’t clear it, these programs offer valuable opportunities:
- Work part-time during your studies.
- Stay in Germany post-graduation to seek employment.
- Begin your journey toward medical licensure in Germany.
This pathway helps you settle in Germany, master the language, assess your medical qualifications, and connect with German state medical councils to pursue a career as a licensed doctor.
Start your journey with us today!
Choose A Best
Suitable Program
- Biomedical Neuroscience
- Biomedical Technologies
- Cardiovascular Science
- Cellular and Molecular Neuroscience
- FOCUS Life Sciences
- International Master in Biomedicine
- Life Science Informatics
- Medical Diagnostic Technologies
- Medical Immunosciences and Infection
- Medical Neurosciences
- Molecular Medicine
- Neurosciences, Experimental and Clinical
- Radiation Biology
- Translational Neuroscience
Choose A Best
Suitable Program
- Biomedical Neuroscience
- Biomedical Technologies
- Cardiovascular Science
- Cellular and Molecular Neuroscience
- FOCUS Life Sciences
- International Master in Biomedicine
- Life Science Informatics
- Medical Diagnostic Technologies
- Medical Immunosciences and Infection
- Medical Neurosciences
- Molecular Medicine
- Neurosciences, Experimental and Clinical
- Radiation Biology
- Translational Neuroscience

We are here to help you!
Open from 8am - 8pm Monday - SATURDAY
Fill out the form below to receive expert advice and guidance.
